In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of societal consciousness, the automotive industry has been striving to develop cleaner and more sustainable solutions.
One such innovation that has made significant strides in reducing vehicle emissions is the closed-coupled catalytic converter.
What is a closed-coupled catalytic converter?
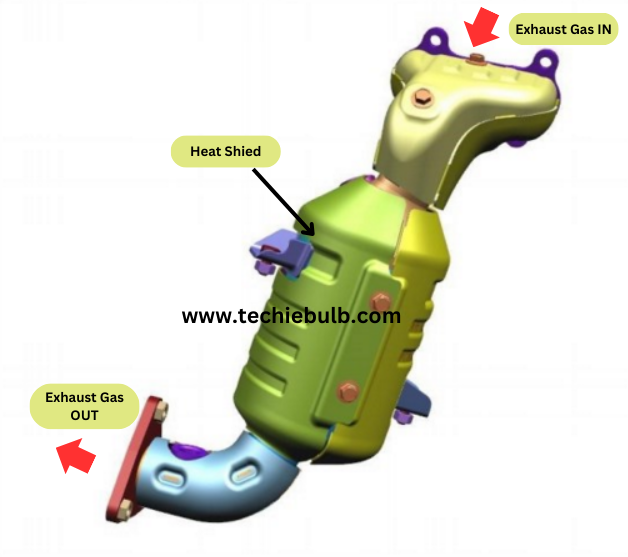
The closed-coupled catalytic converter is a type of catalytic converter used in vehicles to reduce harmful emissions from the engine. It’s called “closed-coupled” because it is positioned close to the engine exhaust manifold, which allows it to reach operating temperature quickly after the engine starts. This quick heating is essential for the converter to become effective in reducing emissions efficiently.
Precious metals Platinum, palladium, and rhodium materials serve as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions that convert harmful exhaust gases, such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and hydrocarbons (HC), into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water (H2O).
The ceramic or metallic substrate provides a high-surface-area structure for the catalyst materials to adhere to, maximizing their effectiveness in catalyzing the exhaust gases. Additionally, the construction of the outer shell of the converter may involve stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant metals to ensure durability and longevity in harsh automotive environments.
The closed-coupled catalytic converter is an integral part of modern vehicle emission control systems, helping to meet increasingly stringent emissions regulations and improving air quality.
Also See:-What is a Partial Zero Emission Vehicle?
How does a closed-coupled catalytic converter work?
Closed-coupled catalytic converters function by utilizing a catalyst to initiate chemical reactions within engine exhaust gases. Positioned near the engine exhaust manifold, these converters quickly reach optimal operating temperatures upon engine ignition, which is essential for efficient catalytic conversion.
As exhaust gases pass through the converter, the catalyst activates, facilitating simultaneous chemical reactions that break down harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and hydrocarbons (HC). Through oxidation, reduction, and other chemical transformations catalyzed by the precious metals, these pollutants are converted into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), and nitrogen (N2).
Ultimately, closed-coupled catalytic converters play a vital role in reducing harmful emissions from vehicles, ensuring compliance with emissions regulations, and contributing to improved air quality and environmental preservation.
Also See:-Limp Home Mode: Meaning, Causes and Diagnostic Explained
What is the design of a closed-coupled catalytic converter?
- Structure: The converter typically consists of a cylindrical or elliptical metal shell with an inlet and outlet for exhaust gases. Inside, there are a series of honeycomb-like structures made of a high-surface-area material, often ceramic or metal coated with catalyst materials.
- Catalyst Material: The most common catalyst materials used are platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which facilitate the conversion of harmful gases like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and hydrocarbons (HC) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water (H2O).
- Closed-Coupled Design: In a closed-coupled configuration, the catalytic converter is positioned as close to the engine as possible, usually directly mounted to the exhaust manifold. This proximity allows the converter to reach operating temperature more quickly after engine startup, improving its efficiency in reducing emissions.
- Heat Shield: Given its proximity to the engine, a heat shield is often employed to protect the converter from excessive heat exposure, which could damage the catalyst material and reduce its effectiveness over time.
- Oxygen Sensor: Many modern closed-coupled catalytic converters also incorporate an oxygen sensor in the exhaust stream before and after the converter. This sensor provides feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion and to monitor the performance of the catalytic converter.
- Monitoring System: The vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system continuously monitors the performance of the catalytic converter. If it detects a drop in efficiency or failure, it triggers a warning light on the dashboard, indicating the need for inspection or replacement.
- Durability and Longevity: To ensure durability and longevity, the materials used in the construction of the catalytic converter must be resistant to corrosion and high temperatures. Additionally, proper maintenance of the engine and exhaust system, such as regular oil changes and fixing any exhaust leaks, can help prolong the life of the converter.
- Compliance: The design must comply with relevant emissions regulations in the region where the vehicle is sold, which may dictate specific performance standards and testing procedures for catalytic converters.
Also See:-What is an Oxygen Sensor in a car?
What are the benefits of a closed-coupled catalytic converter?
Closed-coupled catalytic converters offer several benefits for vehicle emissions control and performance. Positioned closer to the engine than traditional under-car converters, they achieve faster warm-up times, enabling quicker attainment of optimal operating temperatures. This rapid warm-up enhances their ability to efficiently reduce harmful emissions like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons.
Compact design allows for easier integration into the vehicle’s exhaust system, potentially reducing manufacturing costs. By promoting more efficient combustion and reducing exhaust backpressure, closed-coupled converters also contribute to improved fuel efficiency. Crucially, these converters ensure compliance with stringent emissions regulations, helping vehicles meet environmental standards worldwide.
Their close-coupled arrangement optimizes catalyst performance and longevity, further enhancing their effectiveness in reducing pollutants and ensuring cleaner air for all.
What are the signs of a failing closed-coupled catalytic converter?

- Reduced engine performance, such as sluggish acceleration or stalling.
- Increase in emissions leading to failed emissions tests.
- Unusual odors like sulfuric or rotten egg smells from the exhaust.
- Excessive exhaust smoke appearing darker or denser than usual.
- Rattling or clunking noises from the exhaust system indicating internal damage.
- Decrease in fuel efficiency due to restrictions in the exhaust system.
If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to seek professional diagnosis and repair promptly to prevent further damage to the vehicle and ensure compliance with emissions regulations.
Also See:-Battery Thermal Management System
Can a closed-coupled catalytic converter be cleaned or repaired?
Cleaning or repairing a closed-coupled catalytic converter is typically not recommended. Once a catalytic converter fails, it’s usually due to internal damage or deterioration of the catalyst material, which cannot be effectively cleaned or repaired.
In most cases, the only solution is to replace the converter entirely. Attempting to clean or repair a failed converter may result in temporary improvements, but it won’t address the underlying issues causing the failure and could potentially worsen the problem.
Therefore, if a closed-coupled catalytic converter is malfunctioning, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic or automotive technician for proper diagnosis and replacement.
What care should be taken when removing the closed coupled catalytic converter?
- Wear Protective Gear
- Allow the Converter to Cool
- Disconnect the Battery
- Follow the Manufacturer Instructions
- Use Proper Tools
- Support the Exhaust System
- Dispose of Properly
- Inspect Surrounding Components
- Check for Leaks
How often should a closed-coupled catalytic converter be replaced?
Closed-coupled catalytic converters typically do not have a specific replacement interval akin to other vehicle components such as oil filters or brake pads. Their lifespan largely depends on various factors, including vehicle maintenance, fuel quality, driving conditions, and environmental factors.
With proper maintenance and care, a well-maintained catalytic converter can last for the lifetime of the vehicle. However, poor fuel quality, extreme driving conditions like frequent short trips or towing heavy loads, and exposure to harsh environmental elements can accelerate its deterioration.
Generally, catalytic converter replacement becomes necessary if it becomes damaged, physically deteriorated, or fails to meet emissions standards during vehicle inspection. Signs of a failing catalytic converter include the illumination of the check engine light, decreased engine performance, increased emissions, and unusual odors from the exhaust. In such cases, it’s crucial to have the catalytic converter inspected by a qualified mechanic to determine if replacement is necessary.
What is the catalytic converter replacement cost?
The cost of replacing a catalytic converter can vary widely depending on several factors, including the make and model of the vehicle, the type of catalytic converter needed, and where you have the replacement done. On average, you can expect to pay anywhere from $200 to $2,000 for the replacement, including parts and labor.
Some factors that can affect the cost include whether you choose an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) catalytic converter or an aftermarket one, as well as any additional repairs or parts needed during the replacement process. Additionally, labor costs can vary depending on the shop’s hourly rate and the complexity of the installation. It’s advisable to obtain quotes from multiple mechanics or auto shops to ensure you get the best price for your specific situation.
Conclusion
Closed-coupled catalytic converters are indispensable components of modern vehicles, playing a vital role in emissions control and environmental protection. Positioned close to the engine, these converters efficiently reduce harmful pollutants produced during the combustion process, contributing to cleaner air and healthier communities. While their installation may have some implications for vehicle performance, the environmental benefits they offer far outweigh any potential drawbacks. As automotive technology continues to evolve, closed-coupled catalytic converters remain a cornerstone of emissions control, paving the way towards a greener, more sustainable future.




